“Creativity” and “Courage” have become the two most significant motions for success in the 21st century. The number of startup companies increases day by day but only a few of them succeeds. One of the main reasons of business failure is the negligence of legal requirements and unawareness of legal advantages.
5 most frequent legal mistakes made by startup companies are given below:
- Not preparing a shareholders’ agreement
Even though shareholders’ agreement is not obligatory due to the Turkish Legislation, preparing a written agreement would avoid disputes that may occur between shareholders in future. Shareholders may determine important and confidential issues such as percentages, responsibilities, pre-emptive rights, drag-along and tag alone rights, restrictions on transfer of shares etc. by executing a shareholders’ agreement.
- Not choosing the suitable entity type
Choosing the suitable entity type according to the scope of business is vital considering that liabilities, requirements and advantages vary due to the entity type. At this point, in order to have a strong legal insfracture, entrepreneurs that start a business in Turkey should first choose the right entity type by taking into consideration the differences given in the table below*.
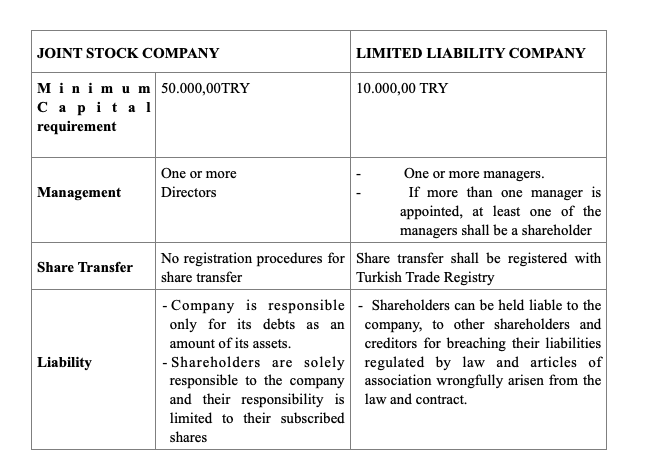
*Table is prepared pursuant to the articles of Turkish Commercial Code numbered 6102.
- Not being protected by intellectual property (IP) rights
Startup companies which do not add intellectual property protection into their business plan are condemned to deal with various problems. Unlike most entrepreneurs think, intellectual property is not only a legal issue but also has an important role for creating value for companies.
A shortlist to protect companies and prevent infringement is given below.
- Running a trademark research before creating a company name
- Taking necessary measures for confidentiality such as signing invention agreements and non-disclosure agreements (NDA) with employees and outside contractors
- Implying internal policies regarding the limitation of access, transfer of information, ownership of work etc.
- Choosing the suitable type of intellectual property right for the business.
- Unawareness of incentives
Turkey aims to encourage entrepreneurs to operate in Turkey by offering plenty of incentives. Unfortunately, most of the startup companies do not know how to benefit from these incentives and this cause unnecessary expenses.
Incentive types that entrepreneurs might be interested in are outlined as follows:
- Investment incentives
- Research and Development (AR-GE) incentives
- Scientific and Technological Research Council Of Turkey (TÜBİTAK) incentives
- Small and Medium Enterprises Development Organization incentives (KOSGEB)
- Free Trade Zones
- Tax incentives regulated under Corporate Tax Law numbered 5520
- Income tax incentives for young entrepreneurs regulated under the Law Amending Income Tax Law and Some Other Laws numbered 6663.
- Inadequate Terms of Use Agreement and Privacy Policy & Not Establishing Efficient Protection Measures for Personal Data
Terms of Use Agreement and Privacy Policy are essential agreements since most of the companies operate through websites. Even if they do not operate through website, companies still create website in order to connect with users/customers. At this point, it is important for companies to determine the scope of responsibility and to set forth rights and obligations of users/customers.
Apart from that companies should collect and use personal data in accordance with the relevant legislation. “Personal data protection” has become a global issue and many countries started to adopt policies and imply legal measures at national level. Turkish Parliament enacted Personal Data Protection Code numbered 6698, dated 24.03.2016 which entered into force on 07.04.2016. Therefore, companies which do not collect and process personal data in accordance with Personal Data Protection Code would be subject to administrative and penal sanctions.
Ayben Arıkan (ayben@bbahukuk.com)
© BBA Law Firm 2016
